Enthalpy Change of Combustion
Combustion happens as the gasoline most commonly a fossil fuel reacts with the oxygen in the air to create heat. There are two kinds of enthalpy of combustion called higher and lower heating value.

Enthalpy Heat Combustion Experiment 4 Energy Level Heat Exothermic Reaction
Brayton cycle or Rankine cycle.

. H t 1202 kgm 3 1 m 3 s 77 kJkg dry air - 28 kJkg dry air 589 kW Imperial Units. Activation energy is denoted by E a and typically has units of kilojoules per mole kJmol or kilocalories per mole kcalmol. The higher heating value takes.
The high energy required for initiation is explained by the unusual structure of the dioxygen molecule. First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is the application of the conservation of energy principle to heat and thermodynamic processes. This is the same as the thermodynamic heat of combustion since the enthalpy change for the reaction assumes a common temperature of the compounds before and after combustion in which case the water produced by combustion is condensed to a liquid.
I highlighted 1 mole of water because thats what I used to solve the problem. From the Mollier diagram we estimate the water enthalpy in the hot air to be 77 kJkg dry air and the enthalpy in the cold air to be 28 kJkg dry air. The first law of thermodynamics in terms of enthalpy show us why engineers use the enthalpy in thermodynamic cycles eg.
DU dQ dW. Using 3 the total sensible and latent heat removed from the air can be calculated as. The lowest-energy configuration of the dioxygen molecule is a stable relatively unreactive diradical in a triplet spin stateBonding can be described with three bonding electron.
The change in internal energy with respect to change in temperature at fixed volume is the Specific Heat at constant volume - c v. Boundary work occurs because the mass of the substance. Constant-volume and constant.
The term activation energy was introduced by. The combustion reaction happens as the fuel and oxygen react creating fire or heat and light. The classical form of the law is the following equation.
According to the definition of enthalpy of neutralization chem libretexts the standard enthalpy change of neutralization is the enthalpy change when solutions of an acid and an alkali react together under standard conditions to produce 1 mole of water. The first law makes use of the key concepts of internal energy heat and system workIt is used extensively in the discussion of heat enginesThe standard unit for all these quantities would be the joule. The heat produced by the combustion of fossil fuels is used in the operation of machineries such as boilers furnaces ovens and engines.
Combustion in oxygen is a chain reaction in which many distinct radical intermediates participate. Unless the pressure is extremely high the work done by applied pressure on solids and liquids can be neglected and enthalpy can be represented by the internal energy component alone. Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required to initiate a reactionIt is the height of the potential energy barrier between the potential energy minima of the reactants and products.
In this equation dW is equal to dW pdV and is known as the boundary work.

Enthalpy Of Combustion Easy Science Learn Physics Chemical Energy Thermodynamics
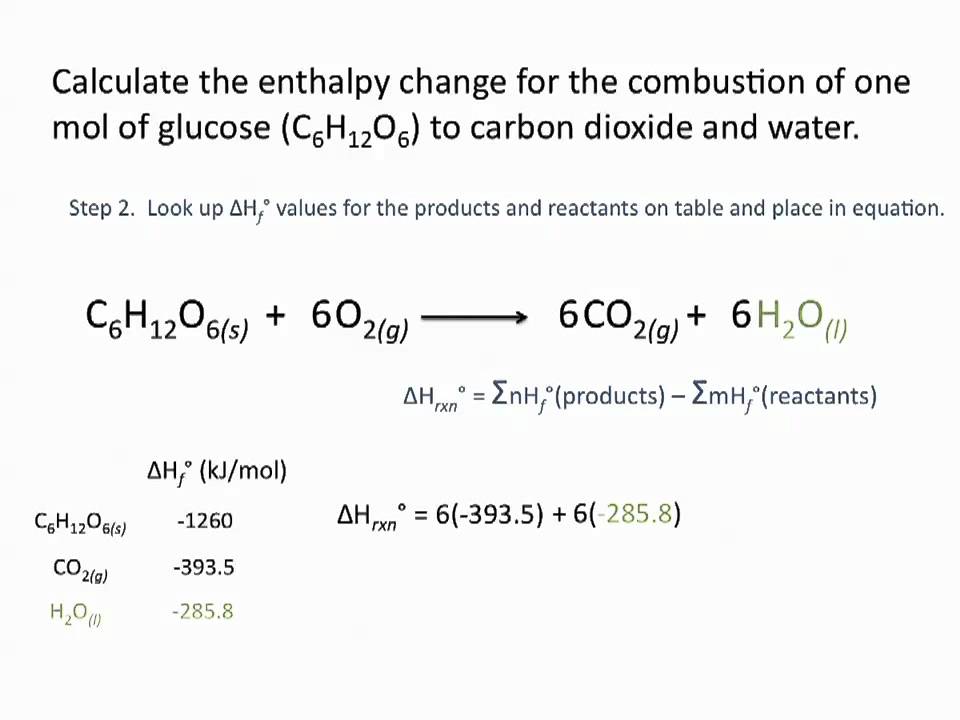
Enthalpies Of Formation Chemsitry Tutorial Science Chemistry Chemistry Tutorial

Total 2 Average 5 X2f 5 What Is The Heat Of Combustion What Is The Definition Of Enthalpy Chemistry Lessons Chemistry Classroom How To Study Physics

Heat Of Combustion Physical Chemistry Chemistry Chemical Equation
0 Response to "Enthalpy Change of Combustion"
Post a Comment